Aluminum vs. Copper Heat Sinks: What’s the Best Option?

Choosing the right heat sink material is key to managing heat in your electronics. Aluminum and copper are the two most popular options, each with pros and cons. Aluminum heat sinks are light, cheap, and used in many applications. Copper heat sinks have better thermal conductivity, so they’re better for critical areas.
This article will compare aluminum and copper heat sinks, so you can decide which one is right for you. Whether you’re designing a new product or upgrading an existing one, our guide will help you make your choice for your project to succeed.
What Are Aluminum and Copper Heat Sinks? A Quick Introduction
A heat sink absorbs and transfers heat from electrical devices to the surrounding environment. It usually consists of materials with high thermal conductivity, such as aluminum or copper. Heat sinks have a large surface area and a structure that improves heat dissipation.
Copper and aluminum heat sinks have similar purposes but differ in price and thermal performance. Copper has better thermal conductivity, making it ideal for CPUs and cell phone heat sinks.
Aluminum heat sinks are popular due to their effective designs. Manufacturers often use extruded aluminum structures that increase surface area and incorporate fins to boost heat dissipation.
Aluminum vs. Copper: A Detailed Comparison of Benefits and Drawbacks
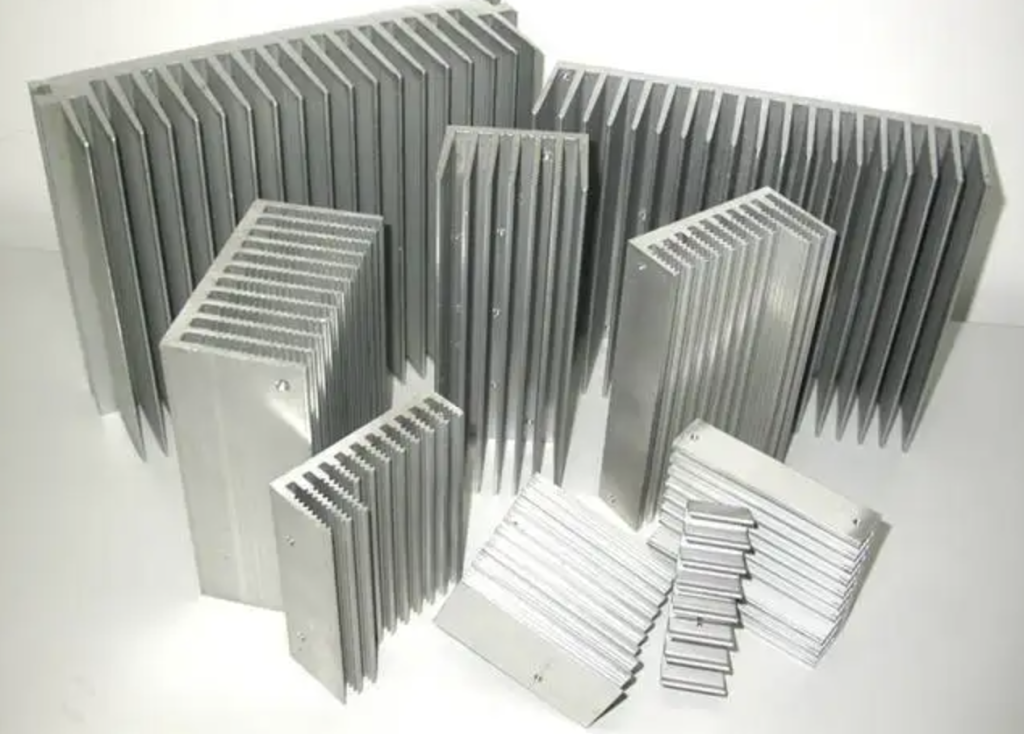

Advantages of Aluminum Heat Sinks
Good Thermal Performance – Aluminum conducts heat well. Its thermal conductivity is three times better than steel and slightly lower than copper. This allows aluminum heat sinks to dissipate heat quickly, lowering equipment temperatures and ensuring proper operation.
Read more: The Role of Aluminum in Heat Management: Heat Transfer & Capacity
Lightweight – Aluminum is lighter than copper. This lower density reduces the overall weight of the equipment when using an aluminum heat sink, making aluminum ideal for cooling cell phones and computers.
Machinability – Manufacturers create aluminum heat sinks using an extrusion process. By changing the mold, they can easily machine them into various shapes and sizes. CNC machining allows for drilling or slotting, meeting the cooling needs of different devices.
Aluminum heat sinks provide effective cooling while being lightweight and easy to customize. These benefits make them a popular choice in many applications.
Disadvantages of Aluminum Heat Sinks
Lower Hardness – Aluminum is softer than copper. This softness makes aluminum heat sinks more prone to deformation or damage from external forces. When impacted, aluminum is more likely to bend or break compared to copper.
Limited Corrosion Resistance – Aluminum has some corrosion resistance, but it is not as effective as copper in highly acidic or alkaline environments. In extreme conditions, copper offers better protection against corrosion.
Aluminum heat sinks have disadvantages, including lower hardness and limited corrosion resistance. These factors can impact their performance in specific applications, so consider your needs carefully when selecting a heat sink material.
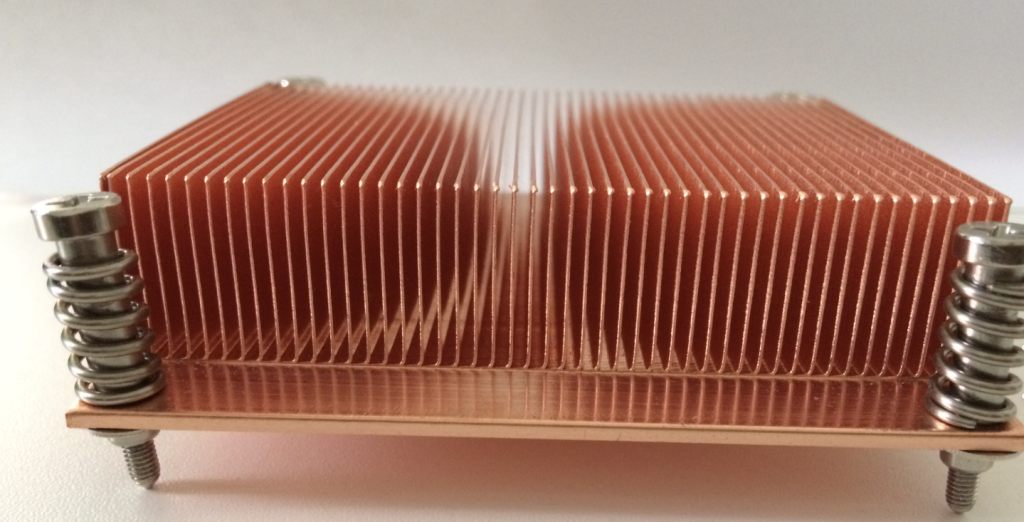
Advantages of Copper Heat Sinks
Excellent Heat Dissipation – Copper has outstanding thermal conductivity. It dissipates heat quickly, which helps maintain stable operation for equipment. This quality is especially useful for large server systems and battery charger heat sinks.
Better Corrosion Resistance – Copper heat sinks resist corrosion better than aluminum. Copper is chemically stable and does not easily react with other metals. Using copper as a heat sink material can extend its lifespan.
Copper heat sinks provide effective heat management and durability. These benefits make them a strong choice for applications that require reliable performance!
Disadvantages of Copper Heat Sinks
Greater Weight – Copper heat sinks can add significant weight to equipment. A large copper heat sink may increase the overall weight of the system, which can impact safety and installation.
Higher Cost – While aluminum is generally less expensive than copper, high-quality copper heat sinks can still be costly. Projects with tight budgets may struggle to incorporate copper heat sinks without exceeding their financial limits.
Copper heat sinks have benefits, but they also come with challenges like weight and cost. Knowing these factors helps you choose the right cooling solution for your needs.
The table below highlights the differences between aluminum heat sinks and copper heat sinks:
| Features | Aluminum Heat Sink | Copper Heat Sink |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Conductivity | thermal conductivity of about 238W/(m·K)(0℃~100℃) | The thermal conductivity is about 397W/(m·K) |
| Density & Weight | 2.7g/cm³ | 8.9g/cm³ |
| Cost | The lower, production cost of 1/4 of copper | Most expensive |
| corrosion resistance | Better, but may be sensitive to some strong acid | Excellent, relatively resistant to corrosion |
| processability | Good formability and ease of manufacture | Difficulty in processing |
| Applications | Lower, production cost of 1/4 of copper | CPU Heat Sink |
| Appearance & Aesthetics | Bright appearance with powder coating or anodized finish | mill finish, may not suit all design styles |
| Safety | Aluminum heat sinks are non-toxic and do not release toxic gases when burned | Burning copper releases toxic gases, but it has a high burning point. |
| Maximum working temperature | 660.4℃ | 1083.4±0.2℃ |
| environmentally friendly | Aluminum alloy or aluminum can all be recycled | High recycling costs |
This comparison shows key factors that influence your choice between aluminum and copper heat sinks. Understanding these differences helps you select the best option for your cooling needs.
How to Choose the Best Heat Sink for Your Project?
When selecting a heat sink, consider your application, equipment needs, budget, and other factors. Here are some tips to help you choose between aluminum and copper heat sinks:
- Budget Constraints: If you have a low budget, choose aluminum heat sinks. Aluminum costs about one-fourth the price of copper. While copper performs better thermally, its higher cost can be a barrier for budget-conscious projects.
- Large Heat Sinks Needed: For large heat sinks, aluminum is the better option because it is one-third the weight of copper. The lighter weight reduces shipping costs and makes installation easier.
- Complex Designs Required: If your project needs complex designs, opt for extruded aluminum. Aluminum extrusion allows for various shapes and sizes that meet specific design needs. Copper is less flexible for intricate designs.
- Longevity Needs: If durability is important, copper heat sinks are superior. Copper can operate at temperatures twice as high as aluminum without losing performance. This capability allows copper heat sinks to effectively dissipate heat over long periods in high-temperature environments.
By evaluating these factors, you can determine which heat sink material best fits your project’s requirements!
Quality Aluminum Heat Sinks to Help Your Project Succeed
Are you looking for high-quality aluminum heat sinks? Do you need help from aluminum heat sink manufacturers? Hugh Aluminum is here for you!
Read more: Aluminum Heat Sink Custom Solutions: Manufacturers, Costs and Benefits
We specialize in extruded aluminum heat sinks. For 14 years, we have worked with companies like ASUS, ABS, HUAWEI, and SUNGROW to produce a wide range of heat sinks.
Our skilled manufacturing team can meet your specific needs. Whether you require standard designs or custom solutions, we are ready to support your project and help it succeed.




