What is the Melting Point of Aluminum? Key Facts and Applications

The melting point of aluminum is 660.3°C (1220.5°F) and that’s why it’s so versatile. When alloyed with copper or magnesium, the melting point can be as low as 500°C or as high as 700°C depending on the alloy. Understanding this is important for construction, automotive, and manufacturing industries as it affects material selection and process efficiency.
At Hugh Aluminum, we offer high-quality aluminum products to meet your specific needs. By using aluminum’s properties, you can improve your project performance. Browse our range of aluminum solutions to get the right material for the job.
What is the Melting Point of Aluminum?
Knowing the melting point of aluminum is important as it affects how the metal behaves in different applications. The melting point is 660.3°C (1220.5°F). With a low temperature like that, aluminum is perfect for industries that require materials that can be easily manipulated or recycled. Whether casting, forging, or recycling aluminum, knowing the melting point is key as it affects the process and outcome of your projects.
Why is the Melting Point of Aluminum Important?
The melting point of aluminum is important for several reasons. First, it determines how aluminum is used in manufacturing and construction. For example, when recycling aluminum’s low melting point, allows it to be melted and reformed without losing quality. This makes aluminum very sustainable as it can be recycled multiple times without losing its properties.
In industries like automotive and aerospace, the melting point is critical for precise temperature control to create strong and durable parts. Knowing this melting point helps you choose the right aluminum alloys and processing methods to get the best performance and life.
With the melting point of aluminum, you can optimize your processes, save energy, and get better results. This is especially important when working with alloys that have different melting points.
Aluminum in Different Industries
Aluminum’s properties, including its melting point, are used in many industries. In the automotive industry, aluminum is used to make lightweight, fuel-efficient vehicles. Its lower melting point allows for casting into complex shapes that increase vehicle safety and performance.
In aerospace, the melting point of aluminum is critical as it determines how the metal performs under extreme conditions. Aluminum is used in aircraft components because it can withstand high temperatures and maintain its structure. Knowing the melting point helps manufacturers choose the right aluminum alloys and processes to meet safety standards.
Aluminum’s flexibility and performance make it a material of choice across many industries.
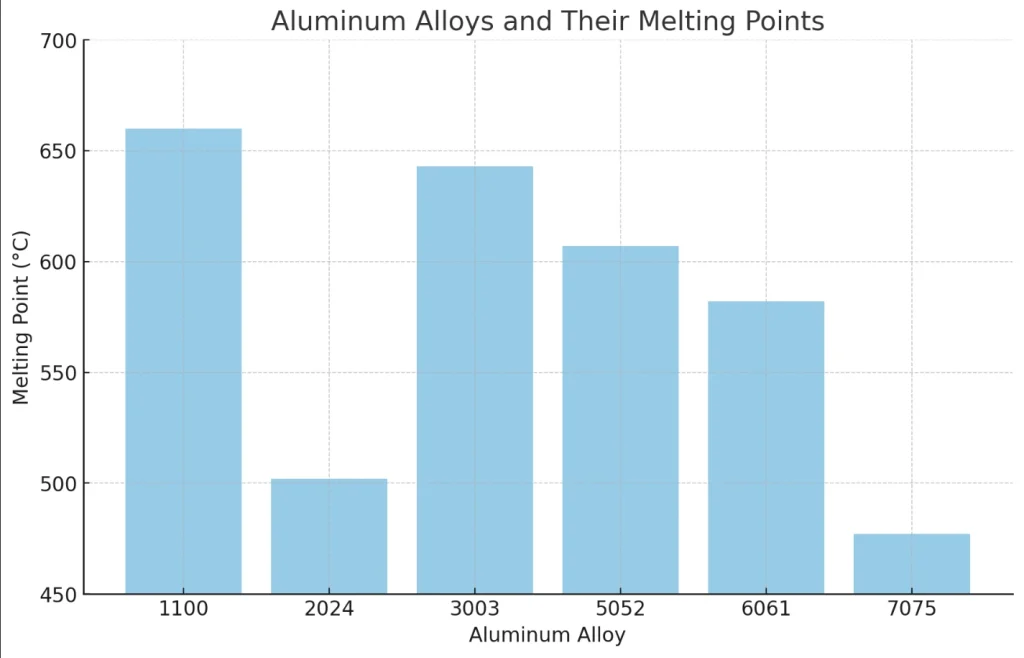
Aluminum Alloys and Melting Points
Pure aluminum has a melting point of around 660.3°C (1220.5°F) but aluminum alloys have a wide range of melting points depending on their composition. This is what makes aluminum alloys so versatile and can be used for various applications.
Wrought Alloys: Melting Point Ranges
| Alloy | Fahrenheit Range | Celsius Range | Applications |
| 2024 | 935 – 1180 | 500 – 635 | High-strength structural applications, aircraft fuselage and wings, gears and shafts, cylinders, and pistons |
| 3003 | 1190 – 1210 | 640 – 655 | Fuel tanks and piping, chemical equipment, heat exchangers, truck and trailer parts, cabinets |
| 5052 | 1125 – 1200 | 605 – 650 | Pressure vessels, marine equipment, fencing, hydraulic tubes, appliances |
| 6061 | 1080 – 1205 | 580 – 650 | Building products, automotive parts, piping, furniture, bicycle frames, railroad cars |
| 7075 | 890 – 1175 | 475 – 635 | Aircraft wings and fuselages, missile parts, gears and shafts, worm gears |
Wrought aluminum alloys are formed into various shapes such as sheets, rods, or wires. These alloys have a melting point range of 500°C to 650°C. The lower end of this range is often associated with alloys that have magnesium in them which lowers the melting point.
For example, 6061 aluminum, a popular wrought alloy, has a melting range of 582°C to 652°C. This range is critical during fabrication processes like welding or forging where temperature control is key to achieving the desired material properties. Knowing these melting points will help you process successfully and get the best out of your projects.
Cast Alloys: Melting Point Ranges
| Alloy | Fahrenheit Range | Celsius Range | Applications |
| A360 | 1030 – 1100 | 557 – 596 | Instrument cases, irrigation system parts, outboard motor parts, hinges |
| A380 | 1000 – 1100 | 538 – 593 | Workbench vises and other hand tools, gear cases, lawnmower housings |
| A413 | 1070 – 1080 | 574 – 582 | Outboard motor pistons, dental equipment, street lamp housings |
| B390 | 950 – 1200 | 510 – 649 | Pistons, blocks, manifolds, and cylinder heads for internal combustion engines, brake cylinders |
Cast aluminum alloys are used to make intricate shapes and have high corrosion resistance. These alloys have a melting point range of 480-600°C. Adding silicon lowers the melting point and increases fluidity so you can cast complex parts.
For example, A356 aluminum, a popular cast alloy, melts between 555-615°C. This range is perfect for automotive parts where precision and durability are key. Knowing the melting point of cast alloys prevents overheating or underheating during the casting process which can lead to defects or subpar products. By knowing these details you can get great results in your aluminum casting projects.
Aluminum Oxide and Its Higher Melting Point
Aluminum oxide, or alumina, has a much higher melting point than pure aluminum so is used in applications where extreme heat resistance is required.
Aluminum vs Aluminum Oxide
Pure aluminum melts at 660.3°C, and aluminum oxide at 2,000°C. The big difference is due to the ionic bonds in aluminum oxide which require more energy to break. So aluminum oxide is used as a refractory in high-temperature applications like furnaces and kilns.
Also, aluminum oxide’s high melting point makes it a good abrasive for grinding and cutting tools. Pure aluminum is good for applications where ease of manipulation and recycling is required, aluminum oxide is good for high-temperature, high-strength applications.
The Electrolysis Process in Aluminum Extraction
Extracting aluminum from aluminum oxide involves a process called electrolysis. This is because aluminum oxide has a high melting point and can’t be extracted directly through conventional melting.
During electrolysis, aluminum oxide is dissolved in molten cryolite, which lowers the temperature required for extraction. The process occurs at around 950°C where an electric current is passed through the solution. Aluminum deposits at the cathode and oxygen is released at the anode. Understanding this process is key to efficient aluminum production.
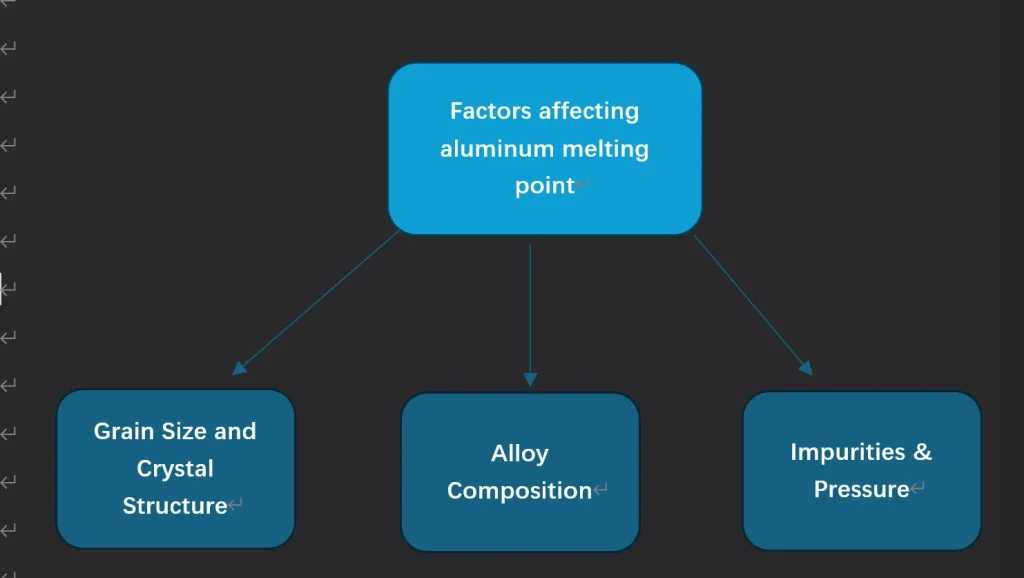
Aluminum Melting Point Factors
The melting point of aluminum is affected by alloying, purity, and heat treatment. Knowing these factors is key to optimizing aluminum for your application and meeting project specs.
Impact of Alloying on Melting Point
Alloying is the biggest factor that affects aluminum melting point. When you mix aluminum with other metals like copper, magnesium, or silicon the resulting alloy can have a different melting point than pure aluminum. For example, copper-aluminum alloys melt between 500-600°C (932-1112°F) and magnesium-aluminum alloys melt between 600-700°C (1112-1292°F). This allows you to adjust the melting point and other properties of aluminum for your application, making it more versatile.
When working with aluminum alloys consider how the addition of other elements will affect the melting point and processing techniques required for best results.
The Effect of Purity and Composition
Purity also affects aluminum’s melting point. High-purity aluminum with minimal impurities will have a more consistent and higher melting point than aluminum with various impurities. Even small amounts of impurities can lower the melting point and change the metal’s behavior during processing.
For example, if your aluminum has trace amounts of iron or silicon you may find the melting point is slightly lower than expected. Knowing the composition of the aluminum you’re using is key as it will affect how you handle and process the material.
Environment
External conditions like temperature and pressure also affect aluminum’s melting point. At standard atmospheric pressure, aluminum melts at its normal temperature. High pressure will raise the melting point slightly and low pressure or vacuum will lower it. These changes are usually small but can be significant in industrial processes.
How Does Heat Treatment Affect Melting Point?
Heat treatment changes the melting point of aluminum. Annealing, quenching, and tempering alter the microstructure of the metal which in turn affects the melting point. During annealing, aluminum is heated to a certain temperature and then cooled down. This relieves internal stresses and increases ductility but can also lower the melting point by changing the grain structure.
Understanding how heat treatment affects the melting point of aluminum is crucial for anyone involved in manufacturing processes where temperature control is critical. By adjusting heat treatment, you can tailor the properties of aluminum to your needs.
Aluminum’s High-Temperature Performance
Aluminum performs well in high-temperature applications, aerospace, automotive, and construction. Its performance is tied to its melting point and behavior under extreme conditions.
What is Aluminum’s Boiling Point?
While the melting point of aluminum is well known, the boiling point is just as important for high-temperature applications. Aluminum has a boiling point of 2467°C (4473°F) which is much higher than its melting point. So aluminum can withstand extreme heat before vaporizing.
In applications like engine components or heat exchangers, the boiling point is critical. It ensures the metal doesn’t degrade under extreme conditions. Knowing both the melting and boiling points helps you make informed material selections for high-temperature situations, safety, and reliability.
Melting Point in Recycling
The melting point of aluminum is important in recycling. Aluminum is highly recyclable and its low melting point makes it easy and energy efficient to re-purpose.
During recycling aluminum scrap is collected, cleaned, and melted above 660.3°C to remove impurities. This can be done multiple times without significant loss of quality making aluminum one of the most sustainable materials available.
By knowing the melting point, you can optimize recycling processes, reduce energy consumption, and contribute to a circular economy. Whether you are in large-scale production or small-scale recycling the melting point is a key factor in efficiency, cost, and environmental impact.
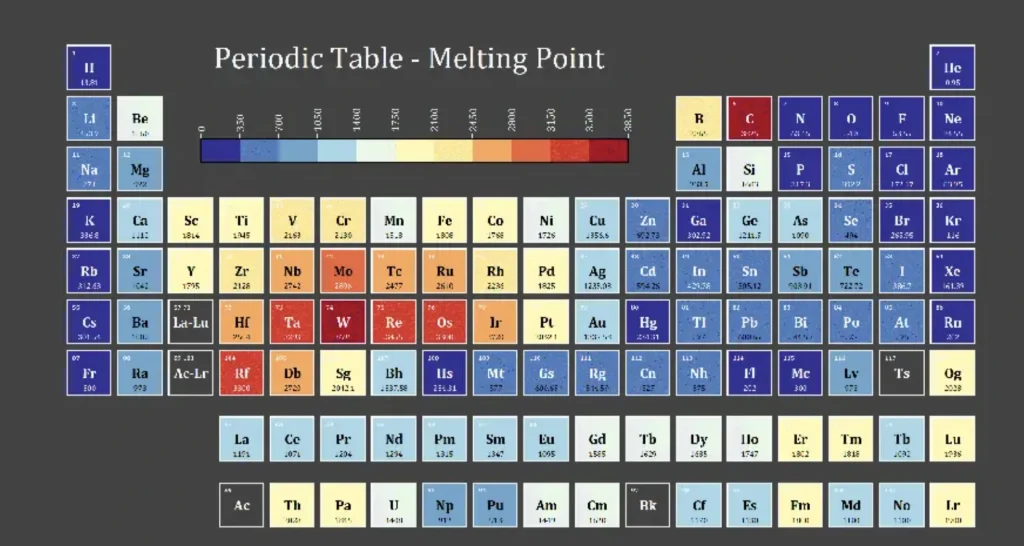
Common Metals and Their Melting Points
Metals have different melting points and understanding these is key when selecting materials for a particular application. The melting point of a metal determines how it can be processed, used and recycled.
Which Metal Has the Lowest Melting Point?
Among common metals, mercury has the lowest melting point at -38.83°C (-37.89°F). This is useful for applications like thermometers and barometers where being liquid at room temperature is an advantage.
Other low melting point metals are tin which melts at 231.93°C (449.47°F) and lead at 327.46°C (621.43°F).
These are used in soldering and other low-temperature applications. Knowing which metals have low melting points helps you choose the right material for heat-sensitive applications.
Which Metal Has the Highest Melting Point?
On the other end of the scale, tungsten has the highest melting point of any metal at 3422°C (6192°F). This is useful for applications where materials need to withstand extreme heat such as light bulb filaments, cutting tools, and rocket engine components.
Other high melting point metals are rhenium and tantalum which are used in high-temperature environments because they can maintain their structure under severe conditions.
When selecting materials for high-temperature applications knowing which metals have the highest melting points is key to durability and performance.
| Metal | Melting Point (°C) | Melting Point (°F) |
|---|---|---|
| Mercury | -38.83 | -37.89 |
| Tin | 231.93 | 449.47 |
| Lead | 327.46 | 621.43 |
| Aluminum | 660.32 | 1220.58 |
| Tungsten | 3422 | 6192 |
| Rhenium | 3186 | 5767 |
| Tantalum | 3017 | 5463 |
Practical Applications of Aluminum’s Melting Point
Aluminum’s melting point is more than just a scientific fact; it’s used in many industries. Knowing how aluminum behaves when heated helps you make better decisions, optimize processes, and produce high-quality products. Let’s look at some key applications where aluminum’s melting point comes into play.
Heat Treatment and Casting
Heat treatment is critical in producing and refining aluminum products. By heating aluminum to specific temperatures, usually near its melting point, and then cooling it under controlled conditions, you can alter the metal’s properties to increase strength, ductility, or hardness.
For example, during annealing, aluminum is heated just below its melting point and then slowly cooled. This process reduces internal stresses and increases ductility making the metal easier to work with.
In casting, aluminum is melted and poured into molds to create complex shapes and components. The low melting point allows for efficient casting with minimal energy consumption and good mechanical properties.
Knowing the melting point allows you to fine-tune heat treatment and casting to get the desired material properties and produce higher quality and more reliable products.
How to Choose the Right Aluminum Grade for Your Project?
Choosing the right aluminum grade for your project is crucial and the melting point is one of the key factors to consider. Different aluminum grades have different melting points based on their composition and alloying elements. This means some grades are better for certain applications than others.
For example, 6061 aluminum has great machinability and moderate strength with a melting range of 582°C to 652°C (1080°F to 1206°F). This is perfect for structural components that need both strength and corrosion resistance.
7075 aluminum has a slightly higher melting point but much higher strength and is used in aerospace where a high strength-to-weight ratio is critical.
So get to know these and choose the right aluminum grade based on its melting point and other properties and you will get better results and your products will meet performance standards.

Why Choose Hugh Aluminum for Your Aluminium Needs?
At Hugh Aluminium, we know how important it is to get the right aluminum for your application. Our range of aluminum products is designed with melting points and other critical properties in mind so we can help you find the right solution for you. Whether you need aluminum for high-temperature applications, complex casting, or special uses, our team has the expertise and materials to help you succeed. You can rely on us to deliver high-quality aluminum products to your exact spec and project.
Final Thoughts
Aluminum’s properties, especially its melting point, is super versatile for many applications. From heat treatment to casting to selecting the right aluminum grade, knowing the melting point is key to optimizing and getting the project done.
By knowing aluminum’s melting point and how it affects different processes, you can use this to improve your work quality and efficiency. Whether you’re in recycling, manufacturing, or product design, knowing these properties will help you make better decisions that will give you better results.
Knowing aluminum’s melting point will not only make you more technical but also innovative and great in your projects. So go ahead and unleash the power of aluminum and let its properties guide you to success.






